Fiber Optic Tech
What Is The Protection of WDM Optical Layer?
To talk about the protection of WDM optical layer, we must first understand the hierarchical structure of WDM optical layer. Here is a figure clearly illustrating the structure of the optical layer.
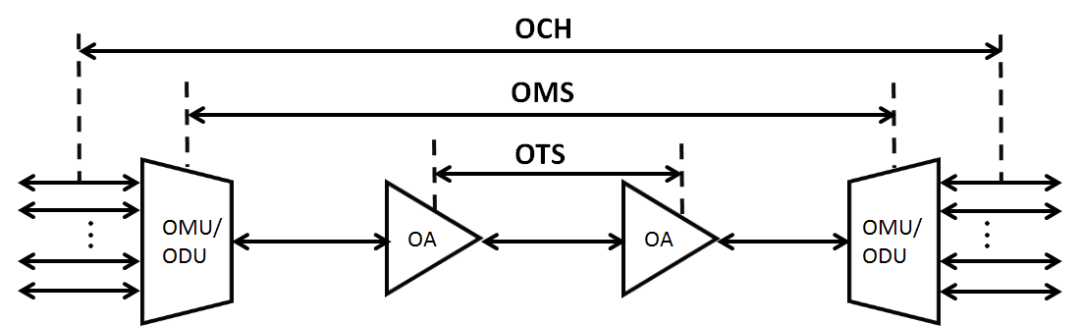
OCH optical channel layer is a single wavelength channel, part between service boards;
OMS optical multiplexing section is composed of multiple OCH optical channels, part between optical multiplexers/demultiplexers OMUs/ODUs;
OTS optical transmission section layer is composed of OMS light monitoring light (if any optical monitoring), part between optical amplifiers OAs and OAs. Therefore, based on the above optical layer structure. There are three types of protection as follows: optical channel layer protection, optical multiplexing section protection and optical transmission section protection
Optical Transmission Protection (also called OLP protection)
Adopt 1+1 dual-transmitting single-receiving or 1:1 transmitting-receiving to achieve the protection of working optical fiber. In 1+1 dual-transmitting single-receiving, single-end switching is adopted, while in 1:1 transmitting-receiving, dual-end switching is adopted (the principles of 1+1 and 1:1 mentioned later are similar).
In OLP protection, no switching protocol is required, so its switching speed is very fast, generally less than 50ms.
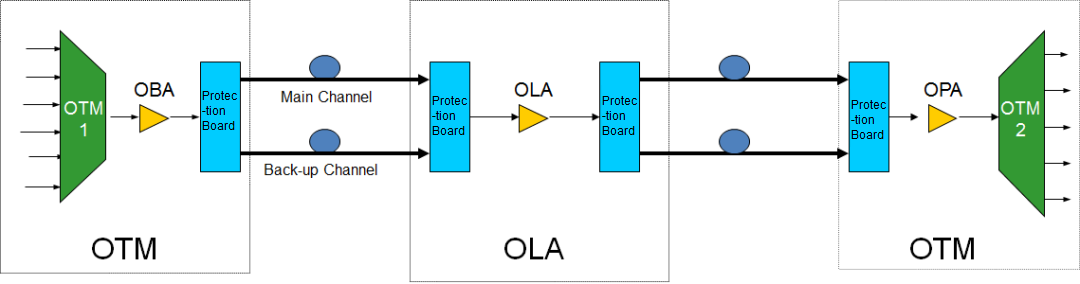
OLP protection is generally used to protect a vulnerable working optical fiber with a spare optical cable.
At the same time, when the OLP board does not need to couple the monitoring light, the protection board of OLP can be basically independent of the main equipment. Therefore, there are many small equipment manufacturers doing this, which just hang directly on the line.In this case, the network management of the main equipment can not manage and monitor the OLP protection process.
Optical multiplexing section protection Protection principle: generally only in the form of 1+1, the transmitting end transmitting OMS light into two, and the receiving end selecting and receiving.
No protection switching protocol is required, because the complexity of network networking is involved, the switching time is not less than 50ms
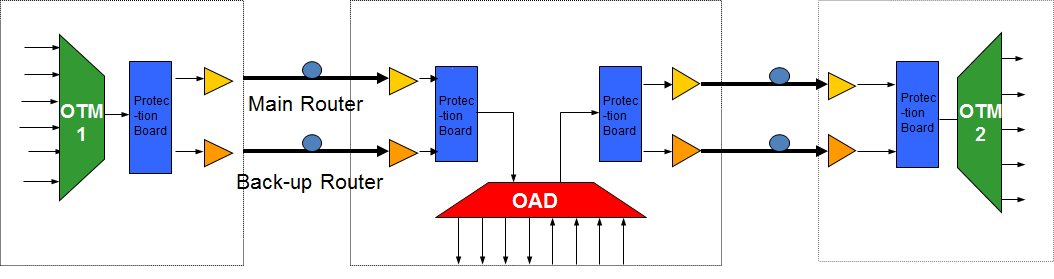
OMS optical multiplexing section protection is generally used to protect the route between OTM/OADM sites. As it is the protection of the section between optical multiplexers/demultiplexers, the spare route also needs to be equipped with corresponding optical layer devices such as optical amplifiers, so this protection consumes a lot of optical fiber resources and equipment resources.
Optical channel protection protection
Divide the service into two parts through the splitter of the protection board, and and receive it at the receiving end through the selection switch. 1+1 and 1:N protection can be achieved in the channel layer.
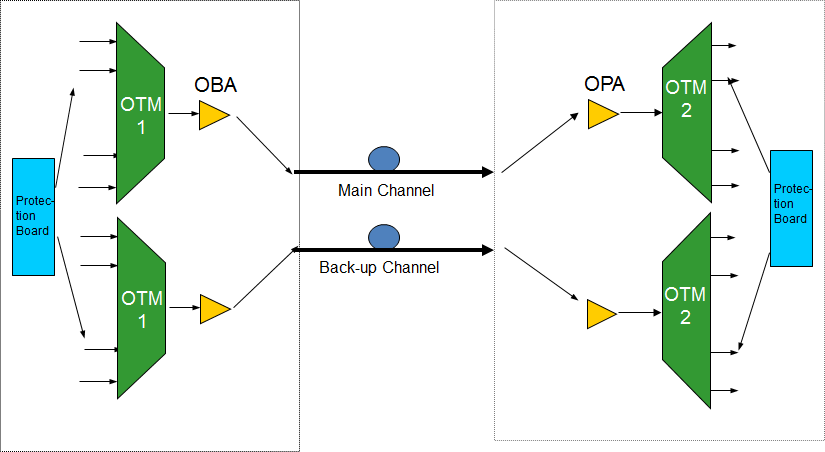
According to the position of the protection board, there are two types of optical channel protection.
One is when the protection board is on the customer service access side, directly dividing the gray light of customer service into two.
The other is when the protection board is after the line board of WDM equipment, dividing the colored light into two.
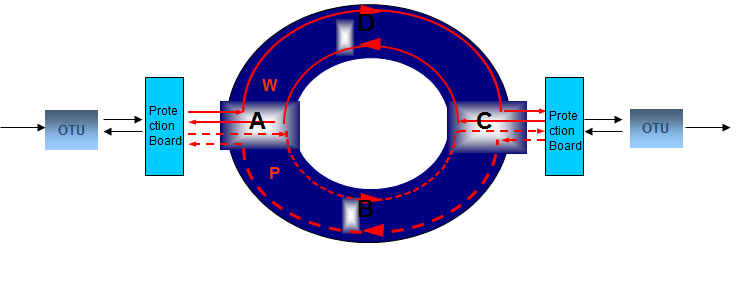
The above are the three common optical layer protection methods.
What is 1+1 protection?
1+1 protection refers to that each main channel has an exclusive standby channel to provide protection for it.The transmitting end simultaneously sends data on the main and standby channels. Under normal circumstances, the receiving end selects the service on the main channel.
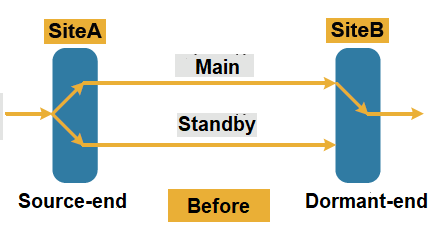
When the main channel is abnormal, the receiving end selects the data of the standby channel according to the channel status and external commands, so that the service can be restored.
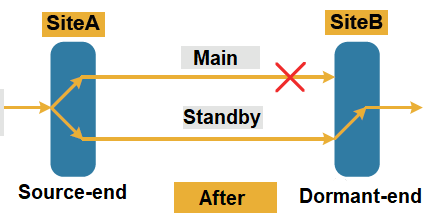
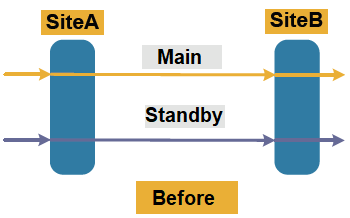
What is 1:1 protection?
1:1 protection refers to that the main and standby channels correspond to each other one by one, protecting each other, but the services are not transmitted on the main and standby channels simultaneously. The transmitting end sends the main service on the main channel and sends the additional service (low-level service) on the standby channel. The receiving end receives the main service from the main channel and the additional service from the standby channel. (M:N protection: that is, M standby channels provide protection for N channels, generally M<=N.)
When the main channel fails, the transmitting end sends the main service to the standby channel, and the receiving end selects the main service from the standby channel. At this time, the additional service is terminated and the main service transmission is restored.
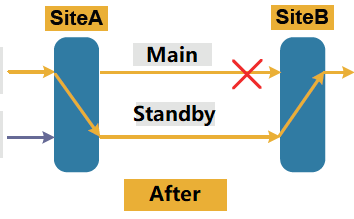
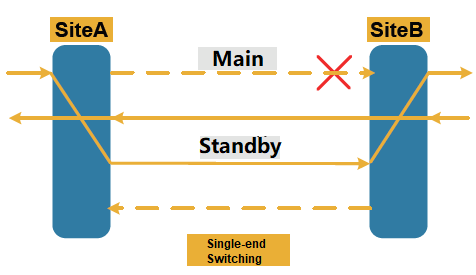
What is single-end switching?
Single-end switching refers to that after a fault occurs in a channel in one direction, only the affected direction is switched, and the other direction remains unchanged, continuing to service from the original channel. Each direction is switched independently without affecting each other. Its advantages are as follows: Single-end switching execution mechanism is simple; no protocol is required; switching speed is fast.
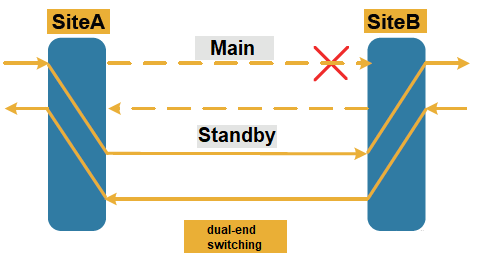
What is dual-end switching?
Dual-end switching refers to that after a fault occurs in a channel in one direction, both directions are switched regardless of whether the other direction is faulty or not. Its advantages are that since both transmitting and receiving are switched, no service will be transmitted in the fault area of the network, and the corresponding fault can be repaired without triggering more protection switching.