Fiber Optic Tech
What is TOSA, ROSA and BOSA in Optical Transceivers
As one of the cores of medium and long haul optical communication, optical transceiver modules play the optical-electric/electric-optical conversion function of optical signals. The interior of transceiver modules is composed of optical devices, functional circuits and optical interfaces, etc. Among the optical components inside the optical module, the major components are the transmitter optical sub-assembly (TOSA) and the receiver optical sub-assembly (ROSA).
TOSA
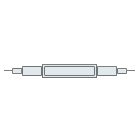
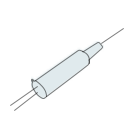
TOSA is the main component of the optical transmitter module, which mainly completes the conversion of electrical signals into optical signals. TOSA can be divided into SC TOSA, LC TOSA, FC TOSA and ST TOSA according to adapter types. TOSA includes optical isolators, monitoring photodiodes, LD drive circuits, thermistors, thermoelectric coolers, automatic temperature control circuits (ATC), and automatic Power control circuits (APT). Among them, the light source (semiconductor light-emitting diode or laser diode) is the core, the LD chip, monitoring photodiode and other components are packaged in a compact structure (TO coaxial package or butterfly package), which then constitutes TOSA.
In TOSA, LD (laser diode) is currently the most commonly used semiconductor emitting device for optical modules. It has two main parameters: threshold current (Ith) and slope efficiency (S). To make the LD work quickly, we must supply the LD with a DC bias current IBIAS that is slightly greater than the threshold current, that is, the laser is emitted only when the forward current exceeds the threshold current.
ROSA
ROSA is the optical receiving component. In high data rate optical modules, PIN or ADP photodiodes and TIA are usually assembled in a sealed metal enclosure to form our light receiving component.
Photoelectric detector, which is the main component of ROSA, is mainly used to convert optical signals into electronic signals through photoelectric effect. Common photodetectors in optical communication are PIN photodiodes and avalanche photodiodes (APD). APD is a highly sensitive photodetector that uses the avalanche multiplier effect to double the photocurrent. The receiver sensitivity of APD can be improved by 6 to 10dB compared to PIN photodiodes.
BOSA
TOSA and ROSA are integrated into the light source transceiver (LD and PIN/APD) through a coaxial coupling process, together with WDM filter, fiber and some other components, they form a BOSA (Bi-Directional Optical Sub-Assembly).

GLSUN offers 1G SFP, 10G SFP+, 25G SFP28, 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28 fiber optical transceiver modules & patch cable solutions to implement optical network connectivity for telecommunication & data center operators.