Fiber Optic Tech
How to Test the Quality of Optical Transceivers
To ensure its quality and performance, each optical transceiver module must go through rigorous testing and quality inspection before shipment. Procedures include incoming quality control, parameter testing, aging test, etc. All test results must be up to standard, otherwise, the optical module will be returned to the production line for adjustment. In this article we will introduce the testing and inspection procedures that an optical transceiver module will undergo, and how the testing results will affect the quality and performance.
1. Incoming Quality Control and Surface Mounted Component Inspection
Incoming quality control and surface mounted component Inspection are performed prior to assembly. Among them, Incoming quality control means that the manufacturer inspects the quality of incoming components before assembling optical modules, such as detect the Transmitter Optical Sub-assembly (TOSA), Receiver Optical Sub-assembly (ROSA), and Bi-Directional Optical Sub-assembly (BOSA) to ensure the quality of optical modules, reduce the rework rate and defect rate as well as avoid damage to expensive optical equipment. Surface mounted component Inspection mainly checks whether the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is correct and whether it is contaminated. This ensures the performance of the optical transceiver module.
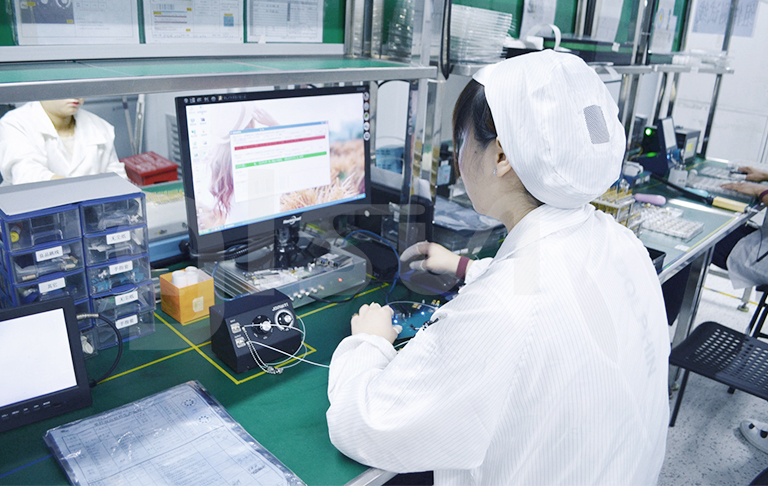

2. Average Output Power Test
The average output optical power is not only an important parameter of the optical module, but also directly affects the quality of communication
3. Extinction Ratio Test and OMA Test
Extinction ratio is one of the parameters used to measure the quality of optical modules. It is the ratio of light power at high level (i.e. full "1" code) and low level (i.e. full "0" code) of laser output, through the test can detect whether the laser is operating in the best bias point and the best modulation efficiency range. In addition, the optical modulation amplitude (OMA) is also a measure of the power difference between laser on and off.
Both are detected by mainstream optical oscilloscopes. At the same time, in the extinction ratio detection can see the relative amplitude of the light signal "1" level and the "0" level, the larger the extinction ratio, the stronger the relative amplitude, the greater the optical signal can be received and distinguished, and the higher the reception sensitivity. Meanwhile,The extinction ratio is inversely proportional to the optical power, and it can be found that the greater the extinction ratio during the test process, the smaller the emitted optical power.
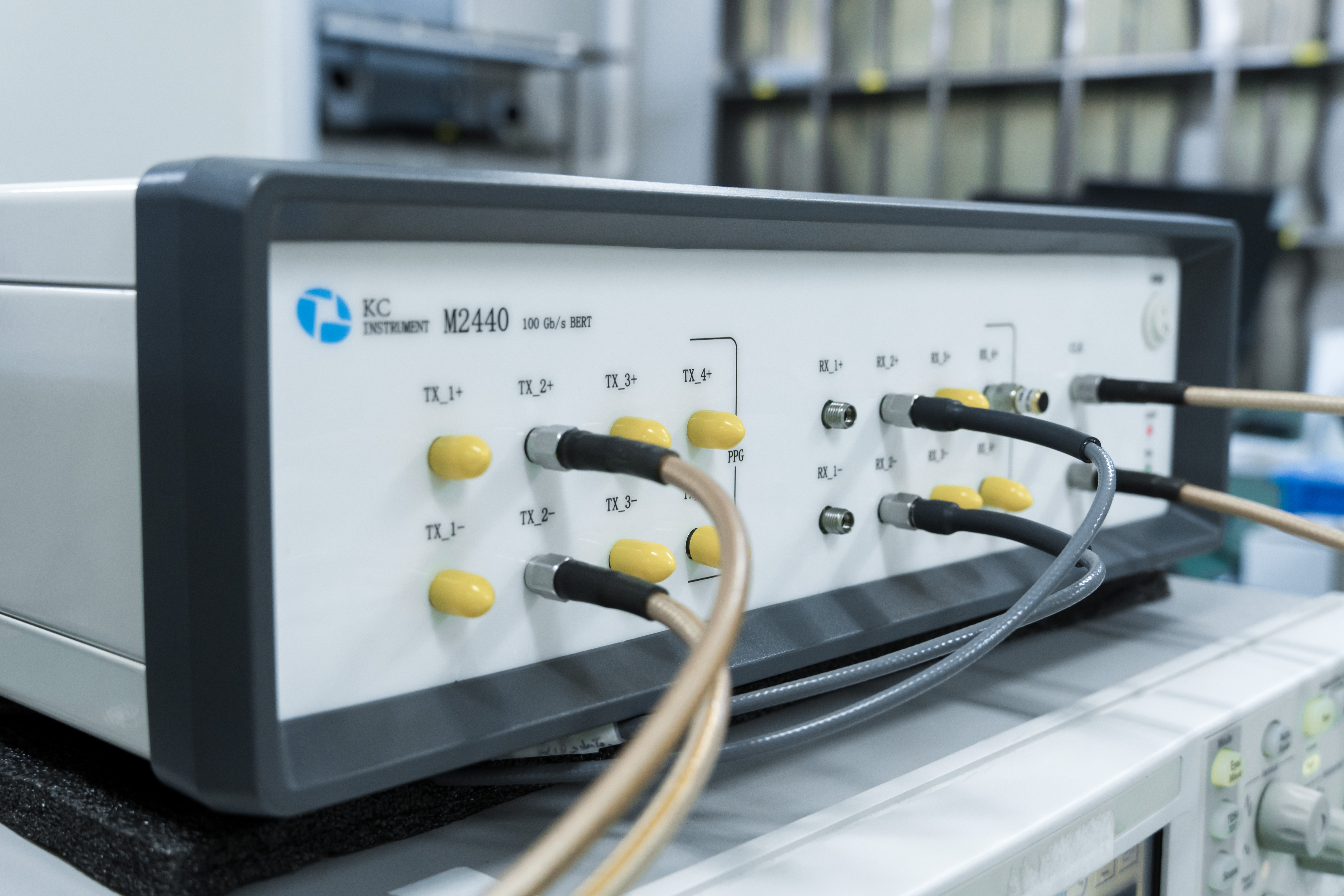
4. Bit Error Rate and Receiving Sensitivity Test
The Bit error rate (BER) is one of the parameters to measure the ability of optical modules to transmit code elements correctly. It refers to the ratio between the number of BER received after photoelectric conversion at the receiving end and the number of BER provided at the output end of the BER. BER test is to receive the pseudo-random signal from the optical module through the standard receiver Test Unit (STU), and then demodulated by the standard receiving tube test unit to complete the bit error rate test.

5. Eye Diagram Test
Eye diagram test and adjustment is an important stage in ensuring that the optical module receives the best signal. The so-called eye diagram is through the persistence function of the oscilloscope to capture all the waveform according to every three bits of superposition accumulation. The digital signal quality of the optical module can be seen from the eye diagram test results, the eye height, eye width, dithering and duty cycle of the eye diagram are carefully observed to judge the performance of the optical module,The larger the eye indicates that the smaller the crosstalk between the codes, the better the performance of the optical module.
6. Wavelength Test
Since the optical transceiver used on both ends of the device must emit the same wavelength to establish communication, the manufacturer must test the wavelength of the optical modules before shipment to ensure that it is within the deviation range.
Generally, manufacturers will use instruments such as spectrometers to measure the central wavelength of an optical module,its measurement will usually deviate from the standard value. Different types of optical module deviation is not the same,but as long as the deviation is within the scope of the permit is approved. If the test value is not consistent with the standard specification, then the optical module is considered defective.
7. Aging Test
Manufacturers generally use photoaging boxes to simulate limit conditions of the optical module testing, to verify the performance of the optical module is up to standard. It is necessary to test the transmitter and receiver after the aging test, mainly to check whether the optical power, extinction ratio, sensitivity and other parameters meet the requirements.
8. Compatibility Test
the optical module into the corresponding brand of switch for detection, and normal communication indicates that the optical module has passed the test. If communication is not possible, the optical module is not compatible with it.
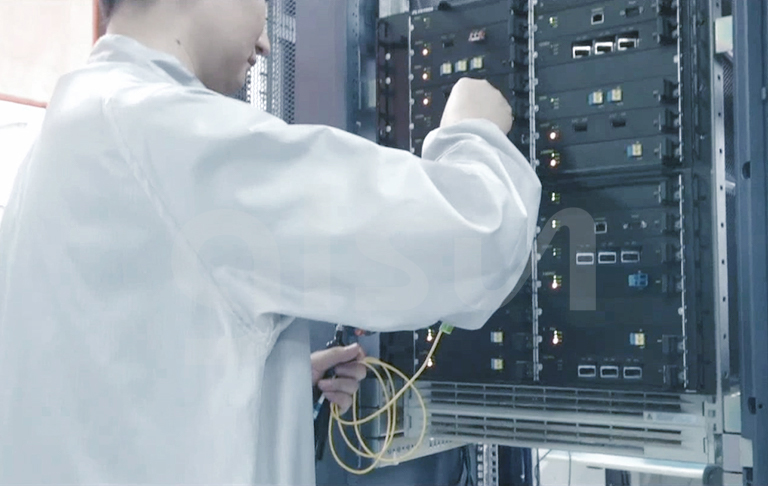

9. End-Face Inspection
After each test item, the end face of the optical module needs to be detected by a microscope for dirt and scratches. If there is dirt, it needs to be cleaned. In fact, each test involves inserting a light module into a device or instrument, which is vulnerable to contamination, so it is necessary to put the optical module under the microscope for inspection before shipment. No dirt can be prepared for packaging shipment, but if there is dirt, it needs to be cleaned.
The above-mentioned tests are all qualified optical module manufacturers need to do, GLSUN as a professional and reliable manufacturer of 20 years, strictly control the quality of optical modules and make sure they pass the above-mentioned tests before shipment.