Fiber Optic Tech
How Does XGS-PON Coexist With GPON and XG-PON?
What is XGS-PON?
XGS-PON is a type of Passive Optical Network (PON) technology. PONs use fiber optic cables to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss. In a PON network, a single fiber optic cable connects a service provider's central office (called an OLT - Optical Line Terminal) to multiple user s (connected by ONUs - Optical Network Units).
XGS-PON, or 10 Gigabit-capable Symmetric Passive Optical Network, is a cutting-edge technology for fiber optic internet access. It offers a significant leap forward in internet speeds compared to its predecessors, GPON (Gigabit PON) and XG-PON (10G-PON).
XG-PON and XGS-PON both belong to the GPON series. From a technical roadmap, XGS-PON is the technological evolution of XG-PON.
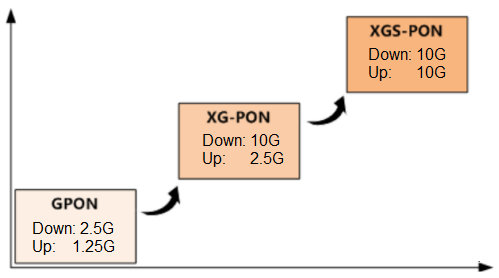
XG-PON and XGS-PON are both 10G PON. The main difference is that,XG-PON is an asymmetric PON, and the upstream/downstream rate of the PON port is 2.5G/10G; XGS-PON is a symmetrical PON, and the upstream/downstream rate of the PON port is 10G/10G.
| Feature | GPON | XG-PON | XGS-PON |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Downstream Speed | 2.5 Gbps | 10 Gbps | 10 Gbps |
| Maximum Upstream Speed | 1.25 Gbps | 2.5 Gbps | 10 Gbps |
| Symmetry | Asymmetrical | Asymmetrical | Symmetrical |
| Maturity | Mature | More advanced | Newest |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Moderately priced | More expensive |
The main PON technologies currently used are GPON and XG-PON, both of which are asymmetric PON. Since the user's uplink/downlink data is generally asymmetrical, taking a certain first-tier city as an example, among the OLT's uplink traffic, the uplink traffic averages only 22% of the downlink traffic. Therefore, the technical characteristics of asymmetric PON are basically in line with the needs of users. match. More importantly, the uplink rate of asymmetric PON is low, the cost of transmitting components such as lasers in ONU is low, and the equipment price is correspondingly low.
However, user needs are diverse. With the rise of live broadcasting, video surveillance and other services, there are more and more scenarios where users are more concerned about uplink bandwidth. Inbound private lines need to provide uplink/downlink symmetrical circuits. These businesses promote the demand for XGS-PON.
XGS-PON is the technological evolution of GPON and XG-PON, and supports hybrid access of three types of ONUs: GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON.
Coexistence of XGS-PON and XG-PON
Like XG-PON, XGS-PON uses broadcasting for downlink and TDMA for uplink.
Since the downlink wavelength and downlink rate of XGS-PON and XG-PON are the same, the downlink of XGS-PON does not distinguish between XGS-PON ONU and XG-PON ONU. The optical splitter broadcasts the downlink optical signal to the same ODN link. For each XG(S)-PON (XG-PON and XGS-PON) ONU, each ONU chooses to receive its own signal and discards other signals.
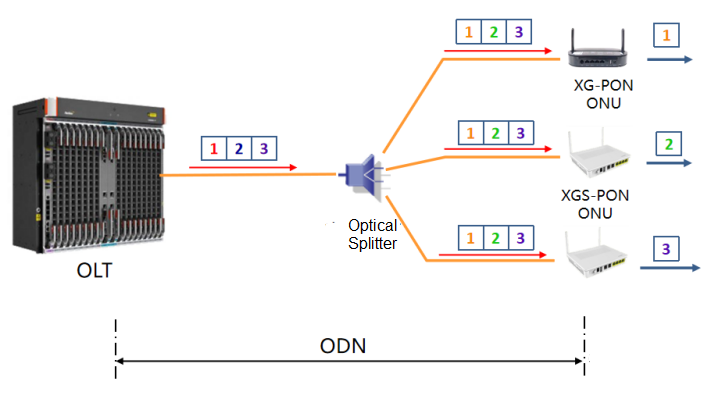
The uplink of XGS-PON transmits data according to time slots, and the ONU sends data within the time slots allowed by the OLT. OLT dynamically allocates time slots based on the traffic requirements of different ONUs and the type of ONU. In the time slot allocated to XG-PON ONU, the data transmission rate is 2.5Gbps; in the time slot allocated to XGS-PON ONU, the data transmission rate is 10Gbps.
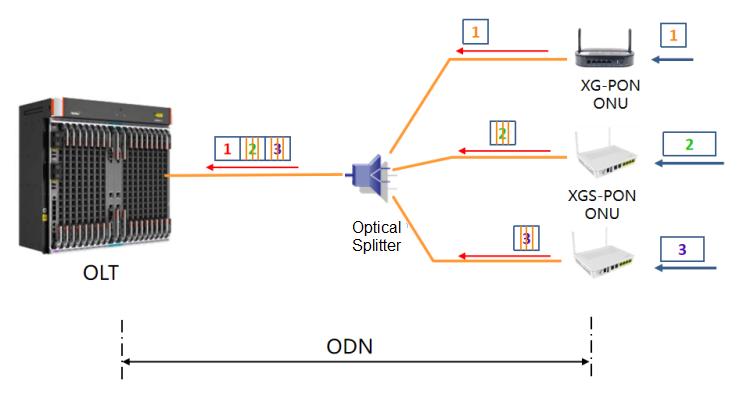
It can be seen that XGS-PON supports mixed access with XG-PON and XGS-PON ONUs.
Coexistence of XGS-PON and GPON
Since the upstream/downstream wavelengths are different from GPON, XGS-PON uses the Combo solution to share ODN with GPON. XGS-PON's Combo optical module integrates GPON optical modules, XGS-PON optical modules and WDM combiners.
In the upstream direction, after the optical signal enters the XGS-PON Combo port, WDM filters the GPON signal and XGS-PON signal according to the wavelength, and then sends the signal to different channels.
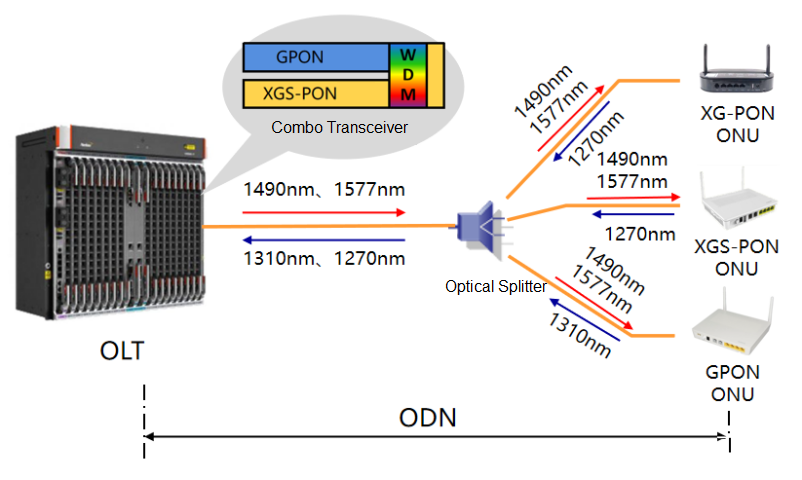
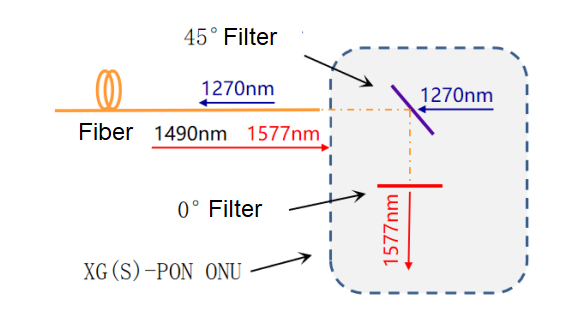
In the downstream direction, signals from GPON channels and XGS-PON channels are multiplexed through WDM, and mixed signals are downlinked to ONUs through ODN. Since the wavelengths are different, different types of ONUs their required wavelengths through internal filters to receive signals.
Since XGS-PON naturally supports coexistence with XG-PON, the Combo solution of XGS-PON supports hybrid access of three types of ONUs: GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON. The Combo optical module of XGS-PON is also called triple Mode Combo optical module (the Combo optical module of XG-PON is called a two-mode Combo optical module because it supports the mixed access of two types of ONUs, GPON and XG-PON).